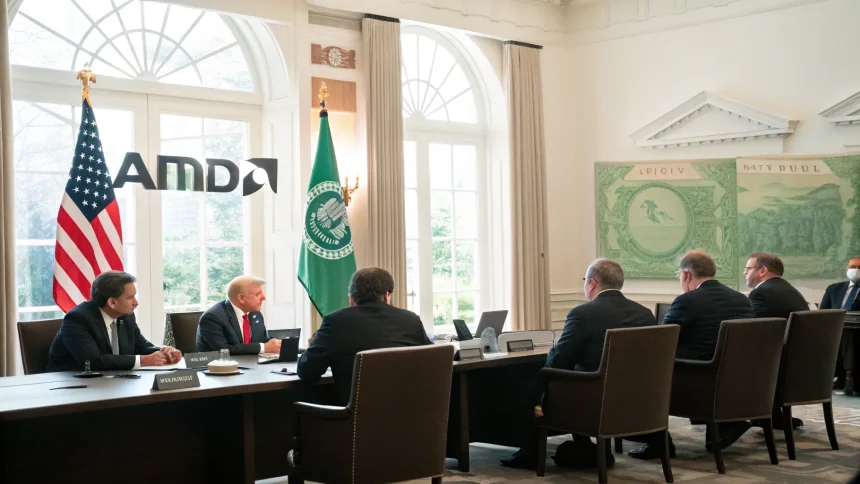
A U.S. government official has confirmed that Nvidia and AMD have reached an agreement to share 15% of their revenues from semiconductor sales to China with the American government. This arrangement marks a significant development in the ongoing tech trade dynamics between the United States and China.
The agreement comes amid heightened tensions over technology exports to China and growing concerns about national security implications of advanced chip technology. Both companies, which are major players in the global semiconductor industry, will now contribute a substantial portion of their China-derived income to the U.S. government under this new arrangement.
The Revenue Sharing Agreement
According to the U.S. government official who confirmed the deal, Nvidia and AMD will transfer 15% of the revenue they generate from chip sales in the Chinese market to the U.S. government. The official did not provide specific details about how this revenue will be collected or allocated once received.
This arrangement represents an unusual step in U.S. trade policy, effectively creating a direct revenue stream from private company operations in China back to the U.S. government. Neither company has publicly detailed how this agreement might affect their pricing strategies or profit margins for products sold in the Chinese market.
Strategic and Economic Implications
The agreement takes place against a backdrop of increasing U.S. restrictions on semiconductor exports to China. In recent years, the U.S. has implemented various controls limiting the types of advanced chips that can be sold to Chinese customers, citing national security concerns.
For Nvidia and AMD, China represents a major market. The revenue sharing arrangement allows these companies to maintain access to Chinese customers while addressing U.S. government concerns about technology transfer and economic benefits.
From the U.S. government perspective, the deal serves multiple purposes:
- Creating a financial benefit from chip sales to China
- Maintaining some oversight of technology flows to Chinese entities
- Establishing a precedent for technology trade arrangements
Industry Reactions
The semiconductor industry has been caught in the middle of U.S.-China tensions for several years. This revenue sharing model represents a new approach to managing these complex relationships.
Analysts suggest this arrangement might become a template for other technology companies operating in both markets. The agreement potentially offers a middle path between complete market access and total restrictions.
Investors will likely watch closely to see how this agreement affects the financial performance of both companies. The 15% revenue share could impact profitability in what has been a lucrative market for U.S. chip designers.
The Chinese government has not yet issued an official response to the arrangement. However, Chinese officials have previously criticized U.S. restrictions on technology sales as attempts to limit China’s technological development.
This agreement represents a new chapter in the complex relationship between U.S. technology companies, the American government, and the Chinese market. As implementation begins, all parties will be watching to see how this arrangement works in practice and whether it achieves the intended balance between commercial interests and national security concerns.