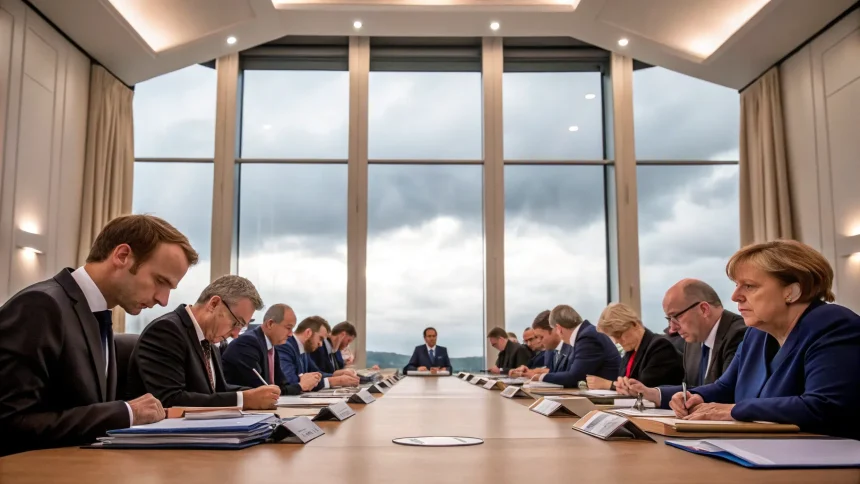
The European Union is preparing to impose new sanctions on approximately six Russian banks and energy companies as part of its ongoing effort to pressure Moscow. This latest round of measures represents a significant expansion of the EU’s economic restrictions against Russia.
According to information from diplomatic sources, the sanctions would target key financial institutions and energy sector companies that play vital roles in Russia’s economy. While specific names of the targeted entities have not yet been publicly disclosed, the move signals the EU’s determination to maintain pressure on the Russian government.
Financial and Energy Sectors in Focus
The proposed sanctions would strike at two critical pillars of the Russian economy – its banking system and energy industry. By targeting these sectors, EU officials aim to limit Russia’s ability to finance its activities and reduce its revenue from energy exports, which constitute a major source of government funding.
Banking sanctions typically include restrictions on transactions, asset freezes, and limitations on access to international financial markets. For energy companies, sanctions often involve restrictions on technology transfers, limitations on investments, and barriers to international cooperation.
An EU diplomat familiar with the discussions stated, “These measures are designed to be precise and impactful, focusing on entities that directly or indirectly support activities that undermine European security interests.”
Coordination with International Partners
The EU is reportedly coordinating these new sanctions with international partners, particularly the United States and United Kingdom, to ensure maximum effectiveness. Previous rounds of sanctions have demonstrated that multilateral approaches create fewer loopholes and apply greater economic pressure.
The timing of the sanctions comes as EU member states have expressed growing concern about Russia’s actions. Several EU officials have emphasized the need for a unified response to maintain credibility and demonstrate resolve.
Economic analysts suggest that while previous sanctions have had measurable impacts on the Russian economy, their effectiveness depends on strict implementation and the ability to prevent circumvention through third countries.
Russian Response and Economic Impact
Russia has typically responded to previous sanctions with countermeasures of its own, including import bans on European goods and restrictions on Western companies operating in Russia. Economic experts anticipate similar retaliatory measures if these new sanctions are implemented.
The potential economic impact of the new sanctions could include:
- Further isolation of targeted Russian banks from international financial systems
- Reduced ability for Russian energy companies to access capital and technology
- Increased pressure on the Russian ruble and domestic inflation
- Complications for European businesses with exposure to sanctioned entities
European businesses with ties to Russia are closely monitoring these developments, with many already having contingency plans in place based on experiences with previous sanctions rounds.
The EU’s decision-making process requires unanimous approval from all member states before new sanctions can be implemented. Diplomatic sources indicate that discussions are advancing, though some countries with stronger economic ties to Russia have expressed concerns about potential blowback effects on their own economies.
As the situation develops, financial markets are watching closely for official announcements about which specific entities will be targeted and the exact nature of the restrictions that will be imposed.