Despite their widespread use in consumer electronics and electric vehicles, conventional lithium-ion batteries continue to present safety concerns due to their flammable components. These power sources, which have become essential to modern technology, contain liquid electrolytes that can pose fire hazards under certain conditions.
Lithium-ion batteries power everything from smartphones and laptops to electric cars, making them a cornerstone of our increasingly mobile and electrified world. However, the same chemistry that allows these batteries to store significant energy in compact packages also introduces safety risks that manufacturers and users must consider.
Understanding the Fire Risk
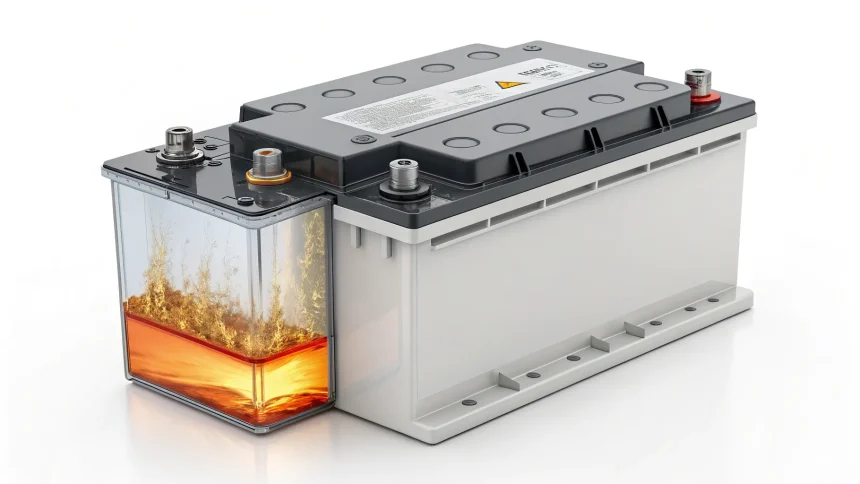
The primary safety concern with lithium-ion batteries stems from their internal structure. These batteries contain a liquid electrolyte that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging cycles. This liquid, typically a mixture of organic solvents and lithium salts, is highly flammable.
When batteries experience physical damage, manufacturing defects, or extreme temperatures, the liquid electrolyte can ignite. This can lead to thermal runaway—a dangerous chain reaction where heat generates more heat, potentially resulting in fires or explosions.
Real-World Incidents
Several high-profile incidents have highlighted these safety concerns. Electric vehicle fires, though rare compared to gasoline vehicle fires, often receive significant media attention. Similarly, consumer electronics manufacturers have issued recalls for devices with batteries prone to overheating.
In 2016, Samsung recalled its Galaxy Note 7 smartphones after multiple reports of batteries catching fire. The aviation industry has also implemented strict regulations regarding the transport of lithium-ion batteries following incidents on cargo and passenger aircraft.
Safety Improvements and Alternatives
Battery manufacturers are working on several approaches to address these safety concerns:
- Improved battery management systems that monitor temperature and prevent overcharging
- Better physical protection to prevent puncture or damage
- Development of solid-state batteries that replace flammable liquid electrolytes with solid alternatives
- New separator materials that can prevent internal short circuits
Solid-state battery technology represents one of the most promising long-term solutions. By replacing the flammable liquid electrolyte with a solid material, these batteries could virtually eliminate fire risks while potentially offering higher energy density and faster charging.
Consumer Safety Practices
While manufacturers work on technological solutions, consumers can take steps to reduce risks when using lithium-ion powered devices:
Using manufacturer-approved chargers and cables helps prevent overcharging and overheating. Avoiding extreme temperatures—not leaving devices in hot cars or exposing them to freezing conditions—extends battery life and reduces fire risk. Watching for signs of battery damage, such as bulging, leaking, or unusual heat during charging, can prevent incidents.
For electric vehicle owners, following manufacturer guidelines for charging and having regular maintenance checks of the battery system are important safety practices.
Despite these concerns, lithium-ion batteries remain relatively safe considering their widespread use. The benefits of portable power and electric transportation continue to drive innovation in battery technology, with safety improvements evolving alongside energy density and charging speed advancements.