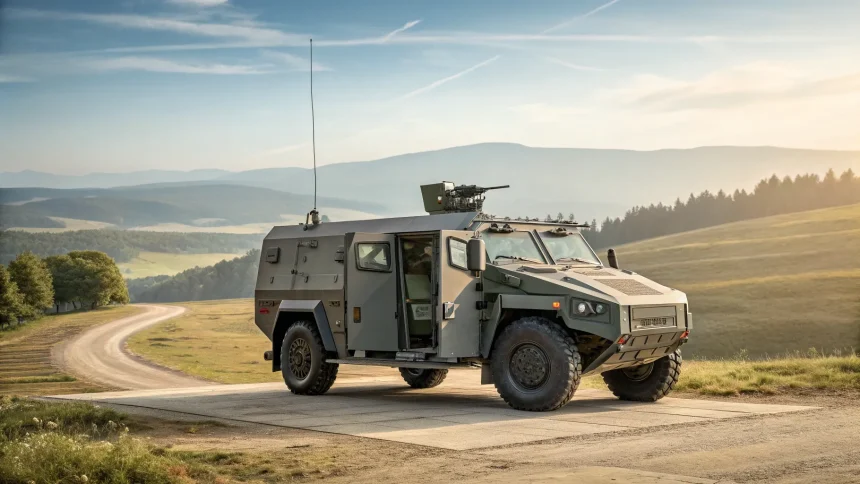
Germany is set to expand its military fleet with an order of 424 wheeled armored vehicles worth almost 7 billion euros, marking one of its largest land systems purchases in years. Finance ministry documents reviewed by Reuters indicate the move could be formalized as soon as this week, underscoring Berlin’s effort to accelerate defense modernization after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
“The German government will order 424 new wheeled armoured vehicles for almost 7 billion euros ($8.11 billion), according to finance ministry documents seen by Reuters on Monday.”
The planned order comes as Germany seeks to meet NATO goals, bolster readiness, and replace aging equipment in the Bundeswehr. It also reflects pressure to replenish stocks and strengthen deterrence along the alliance’s eastern flank.
Context: From Pledge to Procurement
Chancellor Olaf Scholz announced a “turning point” in security policy in 2022, launching a 100 billion euro special fund to upgrade the armed forces. Since then, Berlin has raced to address long-standing equipment gaps, from ammunition to air defense. Large procurement deals have been slow in the past, often facing delays and cost overruns, but the government has pledged faster decisions.
Germany has also committed to spending at least 2% of GDP on defense, aligning with NATO guidance. The armored vehicle buy would fit into that push by improving mobility, protection, and troop transport capabilities across the army’s mechanized units.
- Vehicles: 424 wheeled armored platforms
- Value: Nearly 7 billion euros (about $8.11 billion)
- Average unit cost: Roughly 16–17 million euros
Major land procurements in Germany typically require approval from the Bundestag’s budget committee. The documents described by Reuters suggest the purchase is on a fast track, though delivery timelines and contractor details were not disclosed.
What the Purchase Could Mean for the Bundeswehr
Wheeled armored vehicles give units speed and flexibility on roads and rough terrain. They support infantry transport, command roles, and medical evacuation. A larger fleet could improve Germany’s ability to deploy forces quickly across Europe for training missions or crisis response.
Military analysts say Germany’s forces need modern, reliable platforms that can operate with partners. More standardized vehicles can simplify maintenance and logistics, helping units sustain longer deployments.
Industry, Jobs, and Supply Chain Impact
Germany’s defense industry has reported growing order books since 2022 as European governments rearm. A major armored vehicle contract could support manufacturing jobs and drive investment in supply chains for armor, electronics, and communications systems.
However, suppliers face constraints. Expanding production lines requires skilled labor, component availability, and steady orders. Any slippage can affect costs and timelines. Policymakers will watch how companies manage ramp-ups while meeting export controls and quality standards.
Debate Over Cost and Priorities
Supporters see the purchase as overdue. They argue that armored mobility is essential for NATO commitments and that delays only raise costs. They point to lessons from Ukraine about survivability, redundancy, and rapid repair.
Critics question whether the price tag fits Germany’s budget plans as social and energy costs rise. They warn that maintaining hundreds of new vehicles will add long-term expenses for training, spares, and upgrades. Some lawmakers may push for more detail on lifecycle costs and delivery schedules before giving final approval.
Regional Security and Allied Coordination
Germany’s move aligns with broader European spending increases, with many allies ordering new armored carriers and support vehicles. Combined, these efforts aim to strengthen NATO’s deterrence and its ability to surge forces to the Baltic states and other front-line areas.
Coordination matters. Common systems and standards can improve joint training and interoperability. If Germany’s new vehicles align with allied equipment, it could streamline multinational operations and reduce logistical friction.
What Comes Next
The government is expected to brief lawmakers on costs, financing, and timelines. Questions remain about delivery phases, domestic production content, and the specific variants included. Clarity on those points will shape how quickly units receive new gear and retire older platforms.
For now, the planned order signals that Berlin is converting high-level pledges into concrete contracts. If executed on time and on budget, it would mark a significant step in rebuilding the Bundeswehr’s core capabilities and meeting alliance commitments.
Germany’s defense refresh is far from complete. The outcome of this deal will offer a test of procurement speed, industrial capacity, and political support. Watch for parliamentary review, production schedules, and training plans that determine when troops actually field the vehicles and how they will be used across NATO missions.