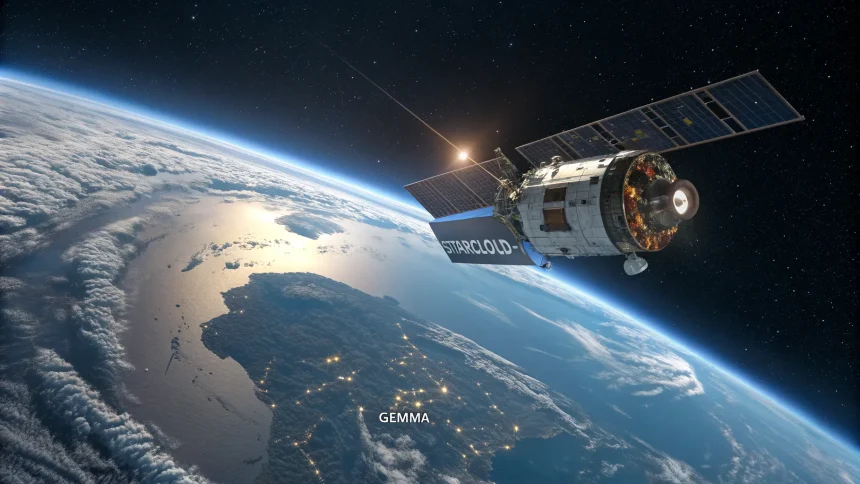
In a first for artificial intelligence and space operations, a company said its Starcloud-1 satellite is running Gemma, an open model from Google, and has trained it while in orbit. The project signals a new phase for on-orbit computing, with AI models learning directly in space instead of only on Earth. The work took place aboard Starcloud-1, though the company has not released many technical details.
The development matters because most satellites still send raw data to ground stations for processing. Training a large language model in orbit could cut the need for constant downlink and allow faster decisions in space. It also points to a future where satellites adapt to new tasks while in flight.
What Was Achieved
“The company’s Starcloud-1 satellite is running Gemma, an open model from Google, marking the first time in history that an LLM has been trained in outer space.”
Gemma is described by Google as an open model family aimed at research and practical use. Running it on a satellite suggests the spacecraft hosts capable onboard computing and a stable software stack. Training in orbit, rather than only performing inference, raises the bar for what space systems can do.
Why Training In Orbit Matters
Space missions deal with tight bandwidth, intermittent links, and strict power limits. AI that learns in orbit can adapt to changing conditions without waiting for ground control. It may classify data on the fly, compress it more efficiently, or update behaviors for autonomy.
Past satellites have used machine learning mostly for inference, such as filtering clouded images or spotting key patterns. Moving to training means the model can improve after launch. That could reduce the volume of data sent to Earth and speed up results for time-sensitive events.
Technical Hurdles And Safety
Training an LLM in space faces hardware and safety challenges. Radiation can flip bits and crash systems. Thermal management is hard in vacuum. Power budgets are tight, and compute loads must be planned around solar and battery cycles. Engineers also need guardrails to keep models from drifting into errors during training.
- Radiation and fault tolerance must protect memory and compute.
- Limited power requires careful scheduling of training runs.
- Thermal control is needed for sustained workloads.
Reliable checkpoints, rollback options, and ground verification are basic steps to keep models stable during updates. If done well, in-orbit training can proceed in small batches, with frequent checks.
Potential Uses Across Space Missions
On Earth observation satellites, an onboard model could learn to spot new patterns in fires, floods, or crop stress and prioritize those images for downlink. Communications satellites might adapt language models to assist with operations or diagnose faults. Deep-space probes could use similar methods to plan routes or manage instruments when contact is delayed.
The approach may also help with data privacy for commercial and government users. Sensitive content could be processed on the spacecraft, and only summaries or alerts would be transmitted. That reduces exposure and saves bandwidth.
Industry Impact And Open Questions
Space companies have been testing edge AI for years, but most efforts focused on small neural networks and pre-trained models. Training a large language model in orbit sets a new benchmark for capability. It may push demand for space-qualified accelerators, better fault-tolerant software, and standardized update pipelines.
Important questions remain. It is not yet clear how much training Starcloud-1 performed, what datasets were used, or how the team measured accuracy. Cost-benefit analysis will depend on the energy spent in orbit versus savings in downlink and ground processing. Standards for validating AI decisions in space are also still taking shape.
What Comes Next
If this approach proves reliable, more satellites may carry hardware to support training and fine-tuning. Agencies and private operators could test task-specific models, from maintenance assistants to onboard planners. Open models like Gemma may see more use because they allow customization and review.
Investors and mission planners will watch for real performance gains. Key signs include lower downlink volumes, faster time to insight, and fewer ground interventions. Clear reporting on safety and testing will be vital to build trust in the method.
The milestone on Starcloud-1 suggests orbital AI is entering a new phase. Training in space could make satellites faster, smarter, and more autonomous. The next steps will hinge on transparency, repeatable results, and careful engineering to manage risk while unlocking practical benefits.