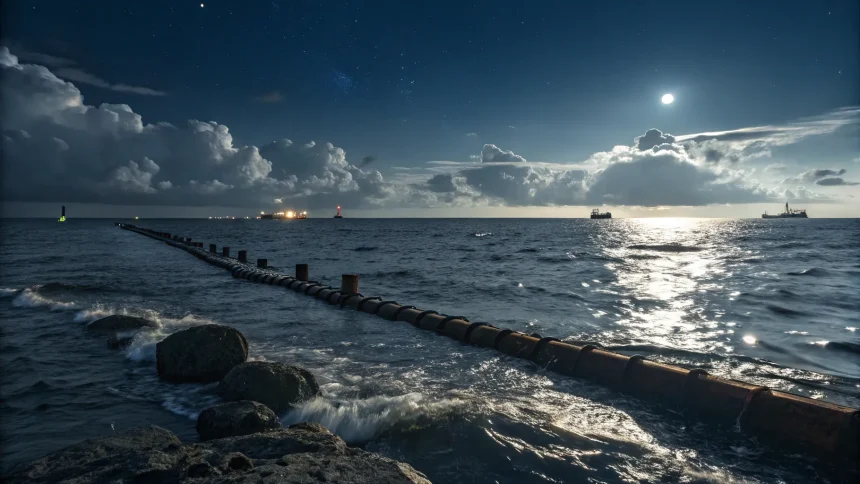
On a late September night in the Baltic Sea, explosions tore open the Nord Stream gas pipelines, severing a major route for Russian gas into Europe. The blasts, which came months after Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, reshaped energy politics, triggered international investigations, and left unanswered questions that still matter for the continent’s security and economy.
“Muffled blasts and a stream of bubbles broke the surface of the Baltic Sea. Explosions had ripped through the two Nord Stream gas pipelines.”
How a Single Night Changed Europe’s Energy Map
The attacks in late September 2022 hit Nord Stream 1 and the unused Nord Stream 2, near the Danish island of Bornholm. Both pipelines run under the Baltic Sea from Russia to Germany. The incident came amid a sharp standoff over energy supplies as Europe rushed to replace Russian gas.
Before the war, Russia supplied about 40% of the European Union’s gas. By 2023, that share fell to well under 15%, according to EU data. Countries pivoted to liquefied natural gas, pipeline imports from Norway, and conservation measures.
The damage put a final stop to a project that had defined Europe’s energy ties with Russia for more than a decade. It also raised fears about the safety of undersea cables and pipelines across the region.
Investigations and Competing Narratives
Sweden, Denmark, and Germany opened parallel inquiries. Swedish prosecutors closed their national probe in early 2024 and shared findings with Germany. Danish authorities said the pipelines were sabotaged but did not publicly name suspects. Germany’s investigation has continued, with limited official detail.
Russia denied involvement and pressed to join the inquiries. Western officials suggested state-level planning was likely, given the depth and complexity of the operation. Media reports pointed to a small team using a chartered yacht, while Ukrainian officials rejected claims of a government role. The United States denied involvement after Russian accusations.
The lack of public indictments has fueled debate. Theories range from state action to a covert group. For now, governments agree on one point: the operation required skill and planning.
Energy Security After the Blasts
European governments moved fast to shore up supplies. New LNG terminals opened in Germany within months. Storage targets were raised and met ahead of winter. Consumption dropped as industries adjusted and households cut use.
- EU gas demand fell sharply in 2022 and 2023.
- Norway became the largest pipeline supplier to the EU.
- LNG from the United States and Qatar filled much of the gap.
Prices spiked after the blasts but eased as mild winters, full storage, and strong LNG flows calmed markets. The episode still changed long-term planning. Governments now treat undersea energy links as critical infrastructure, requiring patrols, sensors, and backup routes.
Environmental and Legal Fallout
The ruptures released huge amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Estimates vary, but researchers say the leaks sent hundreds of thousands of tons into the air. The plumes were visible from space for days.
Ownership and jurisdiction are complex. The pipelines are majority owned by Russia’s Gazprom, with European partners involved in financing. The site lies in waters overseen by Denmark and Sweden, with Germany a central stakeholder. Insurance claims, repair prospects, and liability remain tangled in sanctions and geopolitics.
What It Means for Europe’s Strategy
The blasts accelerated Europe’s shift away from Russian energy and added momentum to renewables and grid upgrades. They also put security at the center of energy policy. Undersea cables that carry electricity and data now face closer scrutiny. NATO has stepped up monitoring and set up a cell to track threats to critical links.
For industry, the shock forced changes in fuel sourcing and efficiency. Some heavy users cut output or switched fuels. Others invested in electrification and heat pumps. The shift could lower gas demand in the long run, but costs and reliability remain concerns.
The Open Questions
The central mystery—who carried out the sabotage—still hangs over the story. Without a public resolution, it complicates diplomacy and policy. It also raises the risk of copycat operations against infrastructure that is hard to guard.
Officials stress resilience. That means more routes, shared reserves, and rapid repair capability. It also means clear rules for investigating and deterring attacks in international waters.
The Nord Stream blasts redrew Europe’s energy and security plans in a single night. Supply chains have shifted, and defenses have tightened. The investigations may yet identify a culprit. Until then, governments and markets are planning for a future where critical infrastructure needs constant watch—and where energy strategy doubles as security policy.