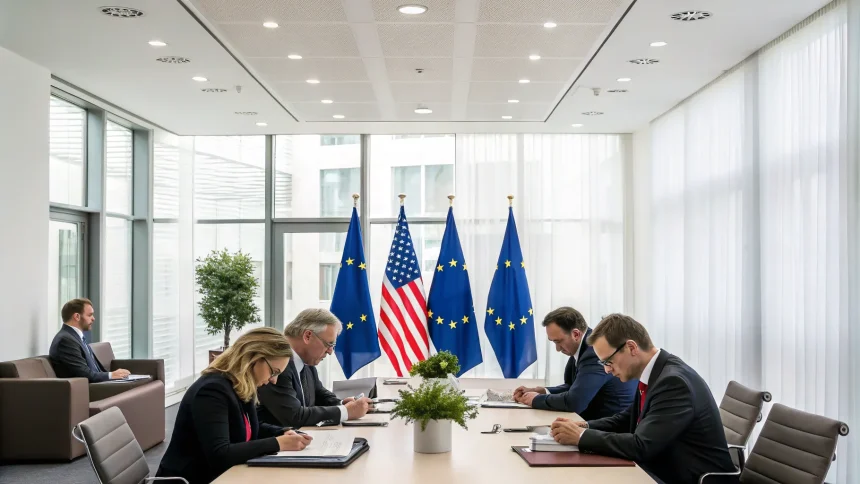
A new trade agreement between the European Union and the United States is generating significant skepticism among European stakeholders as questions arise about its implications for the 27-member bloc.
The proposed deal, which aims to strengthen economic ties between the two major economies, has prompted concerns from various sectors about potential impacts on European industries, regulatory standards, and economic sovereignty.
Rising Concerns Among Member States
Several EU member states have expressed reservations about specific provisions within the agreement. These concerns primarily focus on whether the deal adequately protects European interests or disproportionately benefits American businesses.
Political leaders from countries with strong agricultural sectors, including France and Poland, have questioned whether the agreement might undermine local farming industries through increased competition from American agricultural products.
Meanwhile, consumer protection groups across Europe have raised alarms about potential regulatory changes that could affect food safety standards, environmental protections, and data privacy rules that Europeans have come to expect.
Economic Impact Assessment
Economic analysts are divided on the potential benefits of the agreement. Proponents suggest the deal could boost EU exports to the United States by reducing tariffs and other trade barriers, potentially creating new jobs and economic growth.
Critics, however, point to previous trade negotiations between the two powers, noting that promised economic benefits have sometimes failed to materialize as expected.
“We need to carefully examine whether this agreement truly offers balanced benefits for both sides,” said one European trade official who requested anonymity due to the sensitive nature of ongoing negotiations.
Industry-Specific Concerns
The manufacturing sector has expressed mixed reactions to the proposed agreement. While some industries anticipate expanded market access in the United States, others fear increased competition could lead to job losses in certain sectors.
The automotive industry, a significant economic driver in countries like Germany and Slovakia, has particular concerns about regulatory alignment and potential changes to existing standards.
Digital services and technology companies are monitoring provisions related to data flows and digital trade, as these could significantly impact how European tech firms operate in relation to their American counterparts.
“Any agreement must respect European values and standards. We cannot accept a deal that undermines the protections our citizens expect,” stated a representative from a European consumer rights organization.
Political Challenges Ahead
The agreement faces a complex ratification process, requiring approval from the European Parliament and potentially from national parliaments depending on the scope of the deal.
Political parties across the spectrum have signaled they will scrutinize the agreement closely before lending support. Left-leaning groups have expressed concerns about labor and environmental standards, while right-leaning parties question the impact on national sovereignty.
The timing of the agreement also coincides with broader geopolitical tensions, including ongoing discussions about European strategic autonomy and the changing nature of transatlantic relations.
As negotiations continue, both supporters and critics agree that transparency will be essential to address the growing skepticism. Public consultations and detailed impact assessments may help determine whether the agreement can overcome the current wave of doubt spreading across European capitals.
The European Commission has promised to address these concerns in upcoming negotiation rounds, but whether these assurances will be enough to change public perception remains uncertain as the debate over the trade deal’s merits intensifies.